Firestore Database: Cheat Sheet (Python)
The quickest way to get started with Google’s Firestore Database using Python.
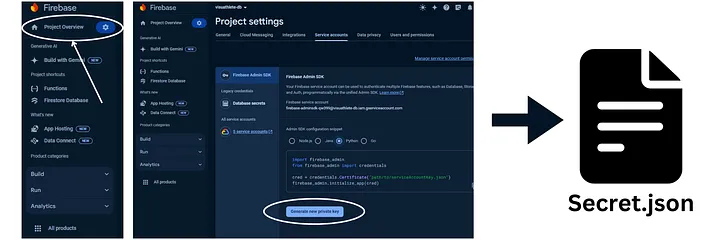
First, authentication. At the top-left, click on the settings icon (Gear wheel) near “Project Overview”. Click on the top option -> “Project Settings”. Click on “Service accounts”, select python and click on “Generate new private key”. This will trigger a json file to be downloaded. In my example, I call it “secret.json”.
SAVE the file and remember its path, it’s essential in order to authenticate with Firestore.
From now on, I will write as little as possible and code as much as possible, so this will be a cheat sheet and not documentation.
Authentication
Write it only once in code. There is no good reason to reconnect to database with each request. Google’s documentation.
import firebase_admin
from firebase_admin import credentials
from firebase_admin import firestore
from google.cloud.firestore_v1.base_query import FieldFilter, Or # for later
# Certification
cred = credentials.Certificate("secret.json") # secret.json = Private key
firebase_admin.initialize_app(cred)
db = firestore.client() # Database reference
Read / Query / Filter Data
Reading data from Firestore database. Google’s Documentation.
col = db.collection("users") # Make sure this collection is in your database
# Get all the docs in a collection
docs = col.stream()
for doc in docs:
document_id = doc.id
document_as_a_dict = doc.to_dict()
name_field_value_example = doc.to_dict()['name']
# Search for a single document in a collection
query = col.where(filter=FieldFilter("name","==","Ilan"))
docs = query.stream()
for doc in docs:
print(doc.id, '->', doc.to_dict())
# Optional: Limit amount of results.
# Better to limit because too much reads per day will be charged
query = col.where(filter=FieldFilter("age","==","24"))
limited_query = query.limit(5)
docs = limited_query.stream()
for doc in docs:
print(doc.id, '->', doc.to_dict())
# Chain two statements with AND
query = col.where(
filter=FieldFilter("age","==","24")).where(
filter=FieldFilter("name","==","Ilan"))
docs = query.stream()
for doc in docs:
print(doc.id, '->', doc.to_dict())
# Chain two statements with OR
filter_1 = FieldFilter("age",">","24")
filter_2 = FieldFilter("name","==","Ilan")
or_filter = Or(filters=[filter_1, filter_2])
docs = col.where(filter=or_filter).stream()
for doc in docs:
print(doc.id)
# Filter a query by searching inside field array
query = col.where(filter=FieldFilter("family_members","array_contains","Josh"))
docs = query.stream()
for doc in docs:
print(doc.id, '->', doc.to_dict())
Reading: Query Operators
As written in firebase docs:
The where() method takes three parameters: a field to filter on, a comparison operator, and a value.
- < less than
- <= less than or equal to
- == equal to
greater than
= greater than or equal to
- != not equal to
- array-contains
- array-contains-any
- in
- not-in
Update Data / Delete a Document’s Field
Update document’s field values with new values, Delete document’s fields, Increment document’s field, Append (Add) to a document’s array field. Google’s documentation.
col = db.collection("users") # Make sure this collection is in your database
# First find the data we want to update
query = col.where(filter=FieldFilter("name","==","Ilan"))
doc = query.get()[0] # get is another way of reading, just like stream()
# Update it
col.document(doc.id).update({
"name": "Daniel",
"age": 20,
})
# Delete a field
col.document(doc.id).update({
"height": firestore.DELETE_FIELD,
})
# Increment a number field
col.document(doc.id).update({
"age": firestore.Increment(1),
})
# Append to an array, using Union
col.document(doc.id).update({
"family_members": firestore.ArrayUnion(["John", "Josh"]),
})
Write Data
Write new data to firebase. Google’s documentation.
col = db.collection("users") # Make sure this collection is in your database
# Add a new document with random-generated id
# Random id example: 02CWbZ9ZukSiHXmYDVFb
col.document().set({
'name': 'Ilan Yashuk',
'age': 20,
'height': 170,
'family_members': ['Jack', 'Daniel']
})
# Add a new document with custom id
col.document("some_id").set{
# ...
})